Here's the kind of thing you should be able to do without a calculator:
Monday, December 28, 2015
Monday, December 7, 2015
Unit 6 Bonding Topics
Bonding Unit Topics
General Bonding:
Octet Rule
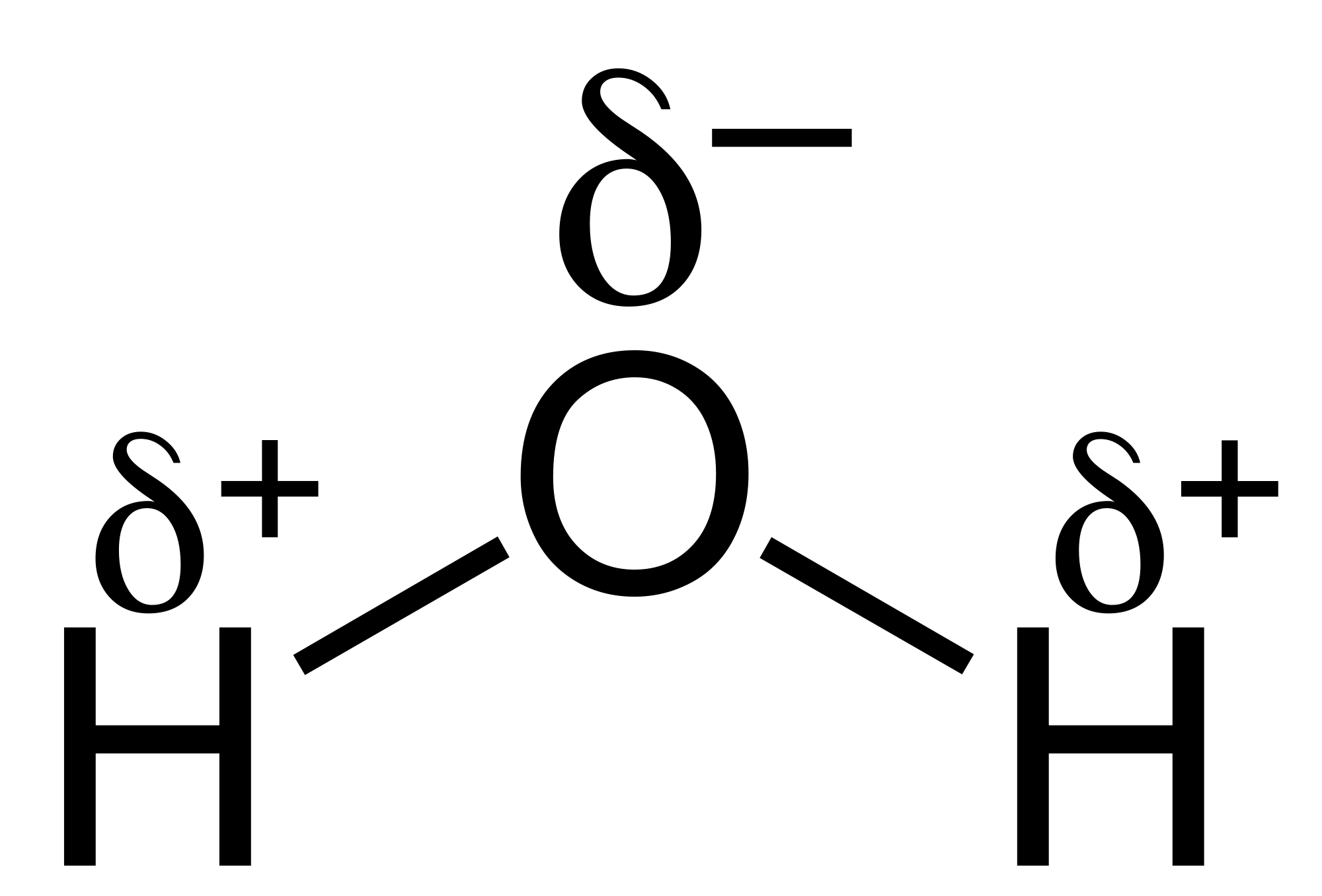
Electronegativity and Bond Type (non polar bonds, polar bonds, ionic bonds)
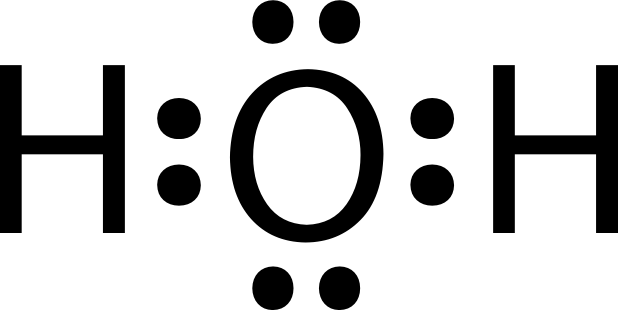
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Valence electrons for each family (Main Group columns: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A)
Electronegativity and Bond Type (non polar bonds, polar bonds, ionic bonds)
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Valence electrons for each family (Main Group columns: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A)
Covalent Bonds:
General properties (gases, liquids or soft solids at room temp)
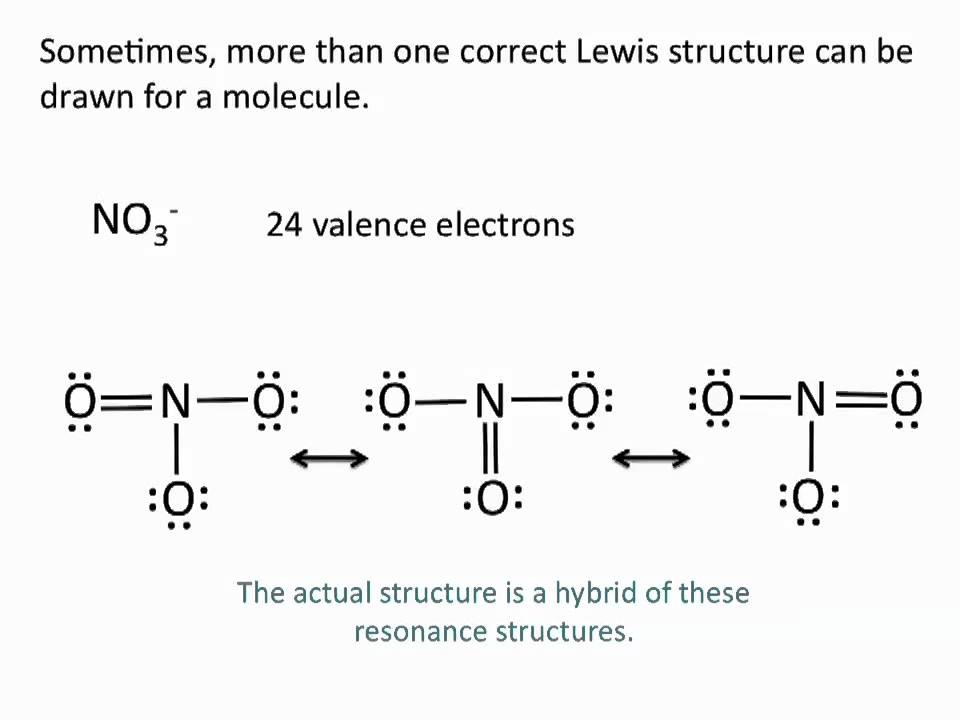
Lewis Structures
Single, double and triple bonds (Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp)
VSEPR shapes (linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, tetrahedral)
Polar vs nonpolar molecules
Ionic Bonds:
Properties of ionic compounds as described by ionic bonds
Brittle Solids at room temperature
High melting and boiling points
Don’t conduct electricity in solid state
Conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in a polar liquid.
Metallic Bonds:
Mobile sea of valence electrons attracted to metal cation
Properties of metals as explained by metallic bonding.
luster, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity
Alloys
Intermolecular Forces (IMF):
London Dispersion Forces
Dipole - Dipole Forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Unit 5 Topics
Topics for Unit 5 - Nomenclature
- Ionic Compounds
- Binary with main group elements
- Binary with Transition Metals
- Polyatomic Ions
- memorize the 'big four'
- Molecular Compounds
- Prefixes and when to use them
- Diatomic 7 (Horses Need Oats For Clear Brown I’s?)
- molecular compounds with common names (H2O, NH3, H2O2)
- Acids
- monoatomic anion
- polyatomic anions
You must be able to go back and forth between name and formula!
Unit 4 Atoms and Light Topics
Atoms and the Periodic Table![]()
Zumdahl Chapter 11: Modern Atomic Theory
Atoms
- Parts of a wave and how they are related to each other
- Wavelength, Frequency, Velocity, and Energy
- The electromagnetic spectrum
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Properties of light and its dual nature
- From gamma rays to radio waves: how does wavelength, frequency, and energy change?
- The visible light spectrum and energy differences between the colors
- The history of the atom
- Scientists contributing to our current model of the atom
- Important experiments and discoveries
- Electron configurations
- principal energy levels and number of electrons that can exist in each
- Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, Hund’s rule
- Write electron configuration for any element or ion (Don’t memorize exceptions, but know that they exist)
- Use the noble gases shorthand when asked
- Electron orbitals
- order of electron filling
- shapes of sublevels (s, p and d)
- number of orbitals (s, p, d, f) (s: 1 orbital l, 2 e-, p:3 orbitals, 6e-, d :5 orbitals, 10 e-, f :7 orbitals, 14 e-)
Periodic Table
- The Periodic Law
- Brief history of development of the modern periodic table
- Families: Names, location on periodic table, characteristics and ion formation
- Alkali Metals
- Alkaline Earth Metals
- Halogens
- Noble Gases
- Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius
- Ionization Energy
- Electronegativity
- Electron Affinity
- Ion size
- Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids (Semiconductors)
- location in periodic table
- basic properties
Unit 3 The Mole, Topics
The Mole and Chemical Reactions
Zumdahl Chapter 6 and Chapter 7
The Mole Chapter 6
Atomic Mass unit
Average atomic mass
Mole
Avogadro’s number
Molar Mass
Molar Mass Conversions
mass to mole
mole to mass
Molar Volume
Empirical and Molecular Formulas
Empirical and Molecular Formulas
Chemical Reactions Chapter 7
Chemical Reaction
Chemical Equation
Reactants
Products
Balancing the chemical equation
Coefficients
Symbols of the physical states (s, l, g, aq)
Unit 2 Chem Skills Topics
Chem Skills Test Topics
Zumdahl Chemistry Text: Chapter 5
Topics:
Scientific Notation
Scientific Notation Calculations
Precision and accuracy
Identifying Significant Figures
Significant Figure Calculations
Metric Conversions
SI Units/conversions
Density Calculations
Specific Gravity
Percent Error
Dimensional Analysis
Unit 1 Review
Topics Covered on Chemistry Foundations Test
Chapters 1-3
- Common Elements/Symbols
- Lab Safety
- States of Matter and characteristics
- Physical & Chemical Changes
- Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures
- examples and definition
- Elements, compounds and mixtures
- Subatomic Particles
- How to find the number of protons, neutrons and electrons
- Charge and location of each subatomic particle.
7. Ions: Cations & Anions (Which common elements form cations and anions and their charges)
- How are ions formed?
8. Isotopes (How to calculate Average Atomic Mass)
- What makes isotopes of an element different than other isotopes?
9. Dependant vs. Independent Variables
- Identification and Graphing (What goes on the x and y axis)
10. Direct vs. Inverse Relationships.
- Shape of graph
- Description of relationship
Image of the Earth from Apollo 17
Today, in 1972, this picture was taken. The famous "Blue Marble" shot.
Blue Marble - Image of the Earth from Apollo 17
Blue Marble - Image of the Earth from Apollo 17
Tuesday, December 1, 2015
Sigma and Pi Bonds: Hybridization Explained!
Video we watched on Tuesday 12.1.15
Monday, November 30, 2015
Brilliant Time-Lapse of Alaska’s Northern Lights
The beautiful interplay of charged particles from outer space (electrons and protons) with single atoms of oxygen! If you're interested, read more at this Wikipedia link.
Topics for Unit 6 Bonding Test
Bonding Unit Topics (Test Dec 4)
General Bonding:
Octet Rule
Electronegativity and Bond Type (non polar bonds, polar bonds, ionic bonds)
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Valence electrons for each family (Main Group columns: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A)
Electronegativity and Bond Type (non polar bonds, polar bonds, ionic bonds)
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Valence electrons for each family (Main Group columns: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A)
Covalent Bonds
General properties (gases, liquids or soft solids at room temp)
Lewis Structures
Single, double and triple bonds (Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp)
VSEPR shapes (linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, tetrahedral)
Polar vs nonpolar molecules
Ionic Bonds
Ionic Crystals
Properties of ionic compounds as described by ionic bonds
Brittle Solids at room temperature
High melting and boiling points
Don’t conduct electricity in solid state
Conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in a polar liquid.
Metallic Bonds
Mobile sea of valence electrons attracted to metal cation
Properties of metals as explained by metallic bonding.
luster, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity
Alloys
Intermolecular Forces (IMF)
London Dispersion Forces
Dipole - Dipole Forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Tuesday, November 24, 2015
Homework due 11.30.15
Read
Chapter 14.1A, pp 489-491
Do
Problems 1, 3, 5, 7 pg 514
note: Practice test for Unit 6 is in Chemistry Locker
Chapter 14.1A, pp 489-491
Do
Problems 1, 3, 5, 7 pg 514
note: Practice test for Unit 6 is in Chemistry Locker
Monday, November 23, 2015
Homework due 11.24.15
Read
Chapter 12.4C, pp 430-433
Do
Problems 50 (b,c), 51, 52 (hint: read the PDF I posted earlier for a direct answer to this) pg 437
Chapter 12.4C, pp 430-433
Do
Problems 50 (b,c), 51, 52 (hint: read the PDF I posted earlier for a direct answer to this) pg 437
Saturday, November 21, 2015
Friday, November 20, 2015
Thursday, November 19, 2015
Wednesday, November 18, 2015
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
Homeword due 11.18,19.15
Read
Chapter 12.3A, pp 413-416
Do
Practice Problem • Exercise 12.2 pg 417 (top of page)
Problems 30, 33, 34 pg 436
Chapter 12.3A, pp 413-416
Do
Practice Problem • Exercise 12.2 pg 417 (top of page)
Problems 30, 33, 34 pg 436
Monday, November 16, 2015
Thursday, November 12, 2015
Wednesday, November 11, 2015
Agenda for 11.12.15
Topics for Friday Test
- Ionic Compounds
- Binary with main group elements
- Binary with Transition Metals
- Polyatomic Ions
- (chart with ions provided)
- Molecular Compounds
- Prefixes and when to use them
- Diatomic 7 (Horses Need Oats For Clear Brown I’s?)
- molecular compounds with common names (H2O, NH3, H2O2)
- Acids
- monoatomic anion
- polyatomic anions
You must be able to go back and forth between name and formula!
Friday, November 6, 2015
Homework due 11.9.15
Read
Chapter 4.2 pp 109-117
Do
Problems 17, 18, 20, 22, 23, 26, 27 pg 119
click here fore awesome ionic naming game!
Chapter 4.2 pp 109-117
Do
Problems 17, 18, 20, 22, 23, 26, 27 pg 119
click here fore awesome ionic naming game!
Monday, November 2, 2015
Homework due 11.4,5.15
Read
Chapter 4.1B, pp 113-114
Do
questions on p 118, #10, 11
Chapter 4.1B, pp 113-114
Do
questions on p 118, #10, 11
Homework due 11.3.15
Read
Chapter 4.1, section A, pp 92-103
Do
Problems 4, 5, 6, 7, pg 118
Chapter 4.1, section A, pp 92-103
Do
Problems 4, 5, 6, 7, pg 118
Friday, October 23, 2015
Homework due 10.26.15
Critical Thinking problems for the Chapter 11 you've already read:
Do Problems 71, 72 pg 396
Be ready for Homework Harvest on Chapter 11. Unit Test next Friday (Oct 30)
Do Problems 71, 72 pg 396
Be ready for Homework Harvest on Chapter 11. Unit Test next Friday (Oct 30)
Monday, October 19, 2015
Homework due 10.20.15
Read
Chapter 11,4, Section C pp 385-390
Do
Problems 48, 49, 50, 54, 56, 57 pg 394
Watch
YouTube video on exploding alkali metals:
https://youtu.be/m55kgyApYrY
[note: some people have stated the video is somewhat fake]
Chapter 11,4, Section C pp 385-390
Do
Problems 48, 49, 50, 54, 56, 57 pg 394
Watch
YouTube video on exploding alkali metals:
https://youtu.be/m55kgyApYrY
[note: some people have stated the video is somewhat fake]
Friday, October 16, 2015
Friday Agenda and Homework for 10.19.15
- Dr. Quantum video
- Einstein's Big Idea "c is for celeritas"
- Quickie Quiz on the videos
- Homework
- Read
- Chapter 11.4, sections A and B; pp377-385 (top of page)
- Do
- Problems 41, 43, 44, 45, 46 pp 393-394
Wednesday, October 14, 2015
History of the Atom PPT/Java Apps
Click here to access the PPT I showed on Tuesday. You need to be on the burlingamehighschool.org account to have access.
Click here to go to download page for the Rutherford simulation app. (Needs Java)
Click here to go to download page for the Hydrogen Atom Model app. (Needs Java)
Click here to go to download page for the Rutherford simulation app. (Needs Java)
Click here to go to download page for the Hydrogen Atom Model app. (Needs Java)
Tuesday, October 13, 2015
Friday, October 9, 2015
Tuesday, October 6, 2015
Homework for 10.7-8.15
Read
Chapter 11.1 pp. 358-365
Do
Problems 2, 5, 7 pg 392
Chapter 11.1 pp. 358-365
Do
Problems 2, 5, 7 pg 392
Wednesday, September 30, 2015
Tuesday, September 29, 2015
Monday, September 28, 2015
The Mole and Chemical Reactions Study Guide
[note: This list is modified from Ms. Marcan's list]
The Mole and Chemical Reactions
The Mole and Chemical Reactions
Zumdahl Chapter 6 and Chapter 7
The Mole Chapter 6 ( 6.1 and 6.2, 6.3 for Gould Students)
Atomic Mass unit
Average atomic mass
Mole
Avogadro’s number
Molar Mass
Molar Mass Conversions
mass to mole
mole to mass
Molar Volume
Empirical and Molecular Formulas (Gould students)
Empirical and Molecular Formulas (Gould students)
Chemical Reactions Chapter 7
Chemical Reaction
Chemical Equation
Reactants
Products
Balancing the chemical equation
Coefficients
Symbols of the physical states (s, l, g, aq)
Predicting products for combustion reactions (not for Gould students)
Predicting products for combustion reactions (not for Gould students)
Practice Test and Quizlets
("Types of Chemical Reactions" not for Gould students in this unit)
("Types of Chemical Reactions" not for Gould students in this unit)
Mole Video Review
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)